The 3 pillars of sustainable development
The concept of sustainable development owes its name to the Brundtland Report of 1987. This report already warned about the negative environmental consequences of economic development and globalisation and tried to find possible solutions to the problems of industrialisation and population growth.
What is Sustainable Development?
This report was drawn up within the framework of the UN World Commission on Environment and Development in 1987. It is in this report that this concept appears for the first time. It is defined as follows:
“Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”.
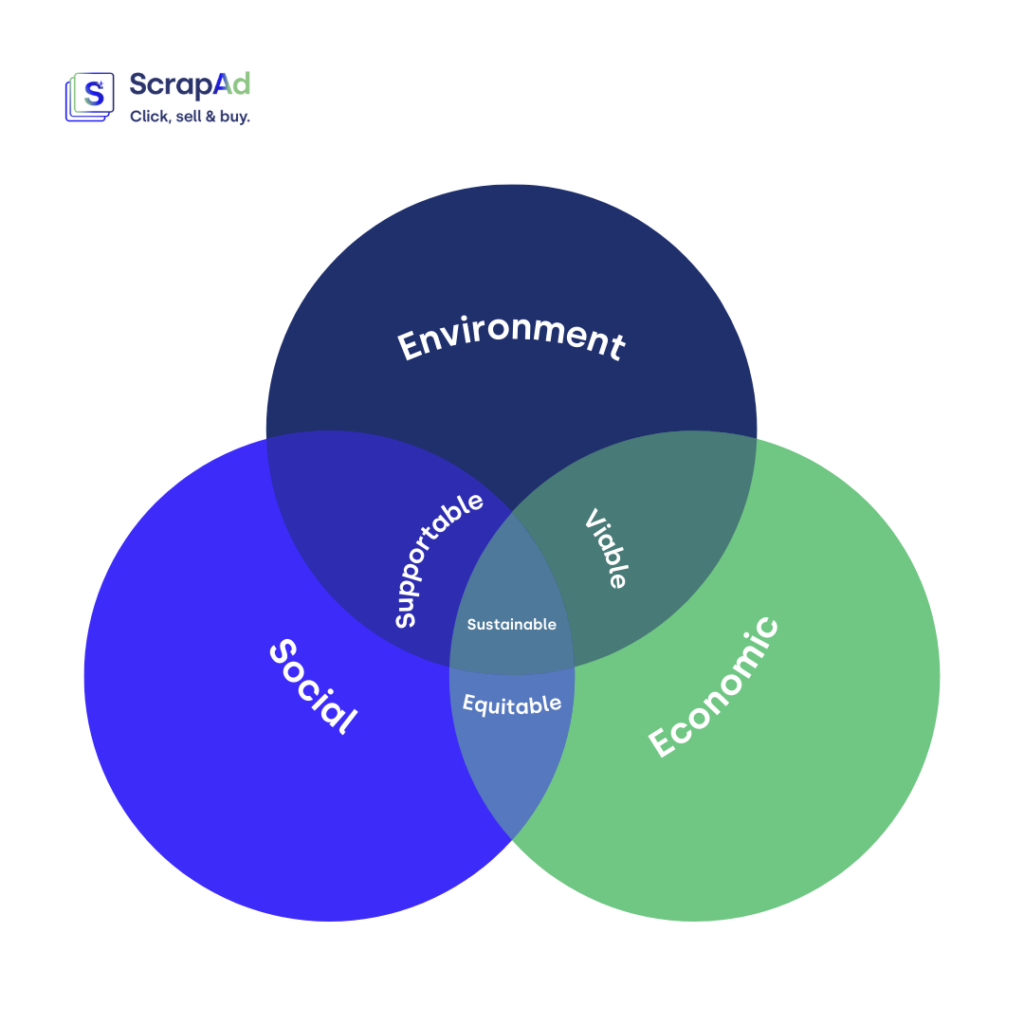
Furthermore, sustainable development has a foundation called the “sustainability tripod”, based on three key areas: economic, environmental and social pillars. Thus, for a company to meet the definition of sustainable development, it must be economically efficient, socially equitable and environmentally sustainable.
Pillars of sustainable development
The pillars of sustainable development must work together in order to meet the ultimate goal: to establish equity between human needs and, at the same time, maintain biodiversity.
Society pillar
This part of the sustainability tripod looks at all people and their quality of life with respect to education, health and basic needs. It seeks to provide the link between the population and their well-being, in order to become a more just society, decreasing the level of poverty and social injustices. The principles of the social pillar are as follows:
- Combating social exclusion and discrimination, assisting reintegration, supporting gender equality and promoting dialogue among others.
- Contribute to the well-being of stakeholders by developing social dialogue, promoting information exchange and transparency.
- Promote solidarity, helping to reduce social inequalities.
Environmental pillar
The environmental pillar is based on the commitment to protect our surroundings and the environment, reducing risks and measuring the negative impact of business activities. Some of the challenges in this area for companies may include:
- Reduce and better manage their waste. It is essential to give each waste the right destination so that it can be recovered and returned to the production cycle. On our ScrapAd platform for buying and selling waste, companies are able to find that counterpart who is interested in the recyclable material they generate or manage.
- Save and preserve natural resources. Raw materials are limited and depleting. It is therefore essential to preserve these resources and use recycled materials.
- Evaluate the carbon footprint and reduce GHG emissions to improve it.
These objectives should appear in the Corporate Social and Environmental Responsibility (CSR) in order to improve their environmental performance.
Economic pillar
The economic pillar aims to increase the well-being of society by employing responsibility through a system of green business. In other words, companies must be able to develop a responsible economic system, producing wealth, but always taking into account human values and respect for the environment and nature.
Sustainability ensures that raw materials are used carefully, but at the same time meeting the needs of the society in which we live.
These three pillars are often represented by a diagram that graphically shows how the three pillars interact with each other and how we see that they support each other. Each of the pillars portrays a context in which sustainability is applied, while at the same time one depends on the other to sustain it.
Culture as the fourth pillar
Culture is seen by many as central to the notion of sustainable development, as it adds to the fundamental aspects of sustainable development explained above.
Culture can also be used as an effective strategy to support the three fundamental pillars. It plays a socially binding and enabling role in the face of economic, social and environmental challenges.